作用
快速切换不同的配置环境,比如开发时是连接的本地数据库,发布线上时是另外的数据库,每次编译打包时都要修该配置文件比较麻烦,这时就可以使用环境隔离了。
一、配置
本地(Local) 开发(Dev) 测试(Beta) 线上(Prod)
打pom文件,添加如下配置
<build>
<resources>
<resource><!--私有配置目录,用变量名来区分-->
<directory>src/main/resources.${deploy.type}</directory>
<excludes><!--排除jsp文件-->
<exclude>*.jsp</exclude>
</excludes>
</resource>
<resource><!--公共配置目录-->
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>dev</id>
<activation><!--默认环境-->
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
<properties><!--对应变量名-->
<deploy.type>dev</deploy.type>
</properties>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>beta</id>
<properties>
<deploy.type>beta</deploy.type>
</properties>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>prod</id>
<properties>
<deploy.type>prod</deploy.type>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
对应的工程目录结构
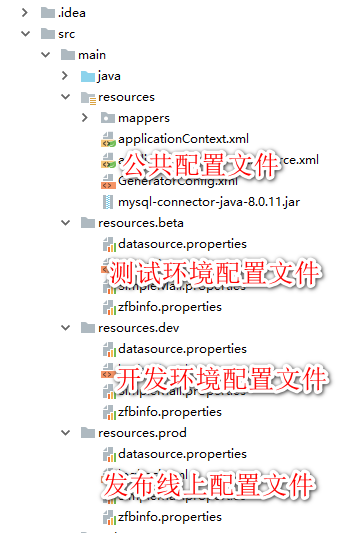
二、编译打包
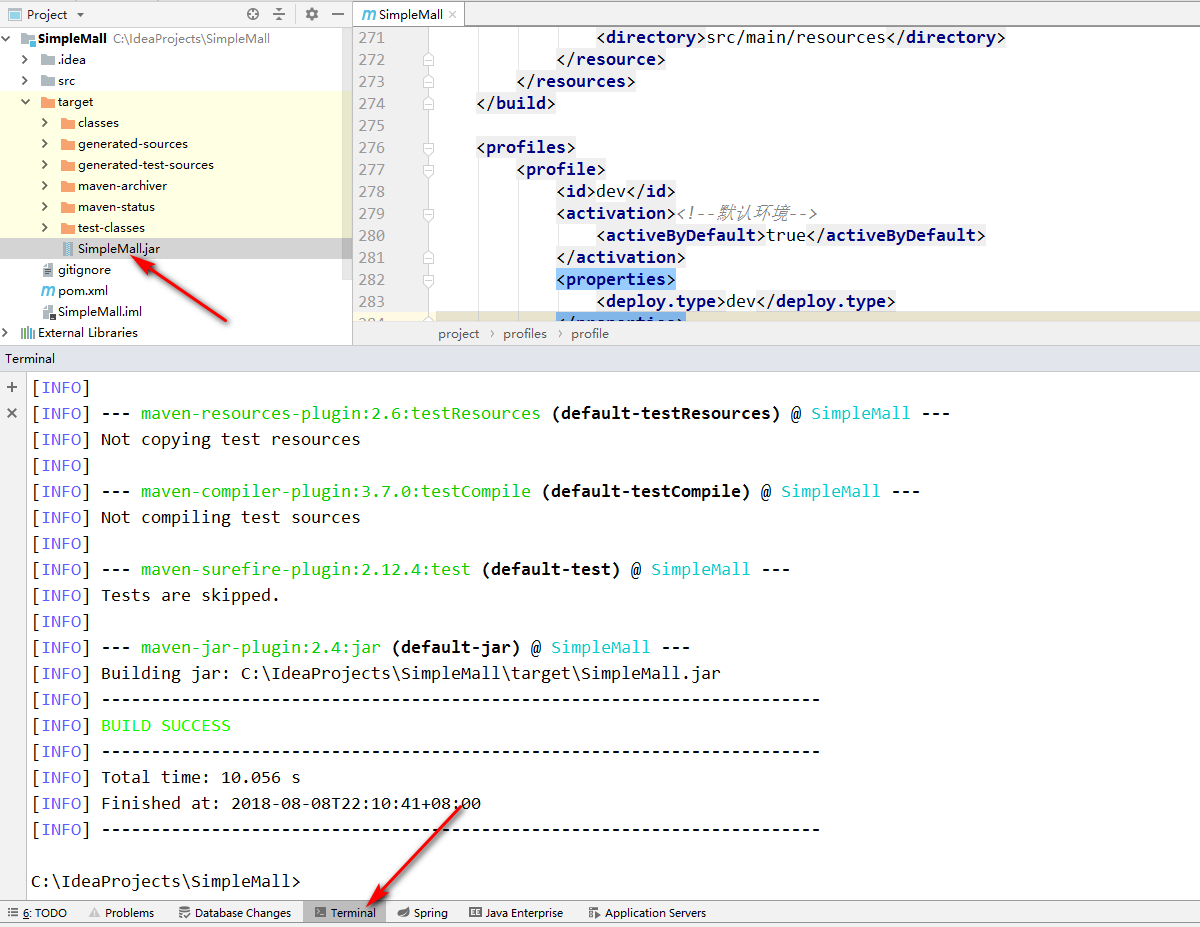
在命令行中输入编译命令,完成后在项目的target文件夹中即可看到jar包
#不编译测试用例类,打包dev环境,改变-P的参数即可切换环境
mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true -Pdev
三、验证
可以在各个环境中放入不同的文件,编译后用压缩包的形式打开jar包查看是否有指定环境的文件。